Disable Tcp Auto-tuning On Windows Xp
- Disable Tcp Auto-tuning On Windows Xp Update
- Windows 10 Tcp Tuning
- Tcp Auto Tuning
- Disable Tcp Auto-tuning On Windows Xp 10
Please enable JavaScript in your browser to use all the features on this site.
Database maintenance for BMO took longer than expected. Thank you for your patience. Please file a bug if something is not working as expected or contact bmo-mods@mozilla.com
Disable Tcp Auto-tuning On Windows Xp Update
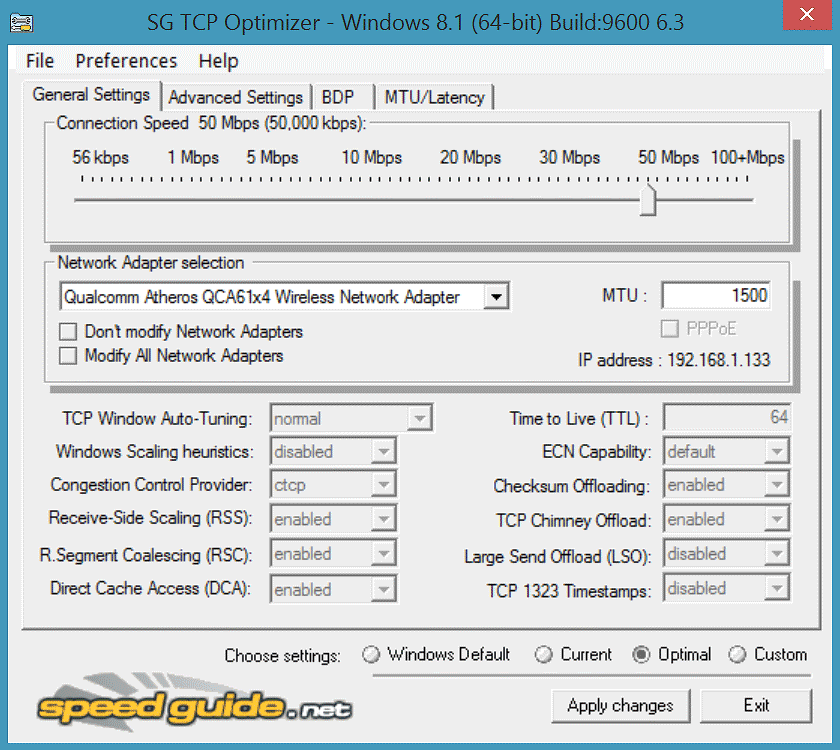
Aug 17, 2016 How to disable ‘Window Auto-Tuning’ on Windows 10. There has been a confusion that using the steps below will improve your internet speeds. Use the Windows key + X keyboard shortcut to open the Power User menu and select Command Prompt (Admin). Type the following command and press Enter: netsh int tcp set global autotuninglevel=disabled. Oct 08, 2016 Receive Window Auto-Tuning popped up with Windows Vista and has been a feature of every Windows version since. I’m going to try and explain this in a VERY oversimplified manner for the non-technical among us. If you want a good full breakdown see: The Cable Guy TCP Receive Window Auto-Tuning Over the internet your info flows through a pipe. Windows TCP Window Scaling Hitting plateau too early. Ask Question. (for TCP in Windows XP and Windows Server 2003) or for each segment acknowledged (for TCP in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008). If you disable 'Receive Window Auto-Tuning' you will be stuck at 64KB packet size which has negative impact over long RTT's in high. Windows Vista includes the Receive Window Auto-Tuning feature which improves performance for programs that receive TCP data over a network. However, this feature is disabled by default for programs that use the Windows HTTP Services (WinHTTP) interface. Some examples of programs that use WinHTTP include Automatic Updates, Windows Update, Remote Desktop Connection, Windows.
Categories
(Core :: Networking, defect)
For bugs in Mozilla's modular networking library (aka 'Netlib' or 'Necko'.) The networking library supplies the software interface that Mozilla uses to access physical transports (e.g. the Internet and local drives), perform URL resolutions, and handle a variety of networking protocols.Examples of appropriate bugs: URLs with backslash not fetched; URLs starting with a single slash turn into http:///; Cannot access authenticated FTP site.
Windows 10 Tcp Tuning
